PlantUML Diagram types
Here’s a summary of PlantUML APIs and syntax for different diagram types, along with key elements to get you started:
Here’s a summary of the key syntax and APIs for different diagram types in PlantUML:
General Structure: Most diagrams start with @startuml and end with @enduml Some specific diagrams have unique start/end tags (e.g., @startmindmap/@endmindmap)
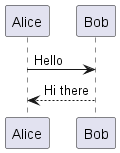
1. Sequence Diagrams
Purpose: Show interactions between objects in a chronological order.
Key Elements:
- Use
->for messages between participants - Use
-->for dotted arrows - Declare participants with
participant,actor,boundary,control,entity,database, etc.
@startuml
Alice -> Bob: Hello
Bob --> Alice: Hi there
@enduml
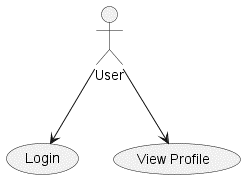
2. Use Case Diagrams
Purpose: Show how actors interact with a system.
Key Elements:
- Define actors with :Actor:
- Define use cases with (Use Case)
- Show relationships with -> or —>
@startuml
:User: --> (Login)
:User: --> (View Profile)
@enduml
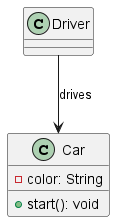
3. Class Diagrams
Purpose: Show classes and their relationships (associations, inheritance, aggregation).
Key Elements:
- Define classes with
class ClassName - Show relationships with arrows like
--,<|--,*--,o--
@startuml
class Car {
-color: String
+start(): void
}
class Driver
Driver --> Car: drives
@enduml
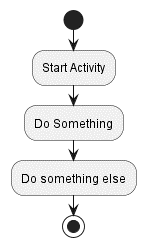
4. Activity Diagrams:
Purpose: Show the flow of activities within a process.
Key Elements:
- Use
startandstopfor beginning and end - Use
if,else,endiffor conditionals - Use
whileandendwhilefor loops
@startuml
start
:Start Activity;
:Do Something;
:Do something else;
stop
@enduml
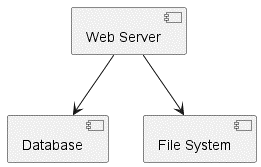
5. Component Diagrams:
Purpose: Show the components of a system and their dependencies.
Key Elements:
- Define components with
[Component] - Show interfaces with
() "Interface"
@startuml
[Web Server] --> [Database]
[Web Server] --> [File System]
@enduml
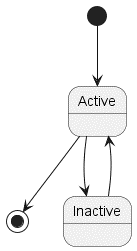
6. State Diagrams:
Purpose: State diagrams visualize the different states an object can be in and the transitions between those states. They are helpful for understanding the behavior of objects over time.
Key Elements:
- Define states with
state StateName - Show transitions with
-->
@startuml
[*] --> Active
Active --> [*]
Active --> Inactive
Inactive --> Active
@enduml
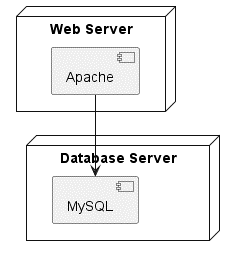
7. Deployment Diagrams:
Purpose: Show the physical layout of a system’s components.
Key Elements:
- Define nodes with
node NodeName - Show artifacts with
artifact ArtifactName
@startuml
node "Web Server" {
[Apache]
}
node "Database Server" {
[MySQL]
}
[Apache] --> [MySQL]
@enduml
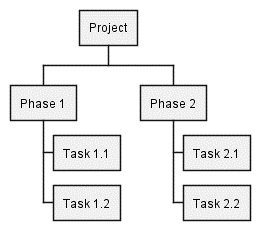
8. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS):
Purpose: A WBS diagram visually breaks down a project into smaller, manageable tasks or deliverables. It helps to visualize the scope of work, dependencies, and relationships between tasks.
Key Elements:
- Start with
@startwbsand end with@endwbs - Use
*for the root node and**,***, etc. for child nodes - Use
+instead of*for alternative notation
@startwbs
* Project
** Phase 1
*** Task 1.1
*** Task 1.2
** Phase 2
*** Task 2.1
*** Task 2.2
@endwbs